CRM in IT has emerged as a game-changer, empowering organizations to elevate customer experiences, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge. By leveraging the capabilities of CRM systems, IT organizations can harness the power of data to enhance customer service, streamline sales and marketing, and drive informed decision-making.
The implementation of CRM systems in IT brings forth a myriad of benefits, including improved customer service and support, streamlined sales and marketing processes, and enhanced data management and analytics.
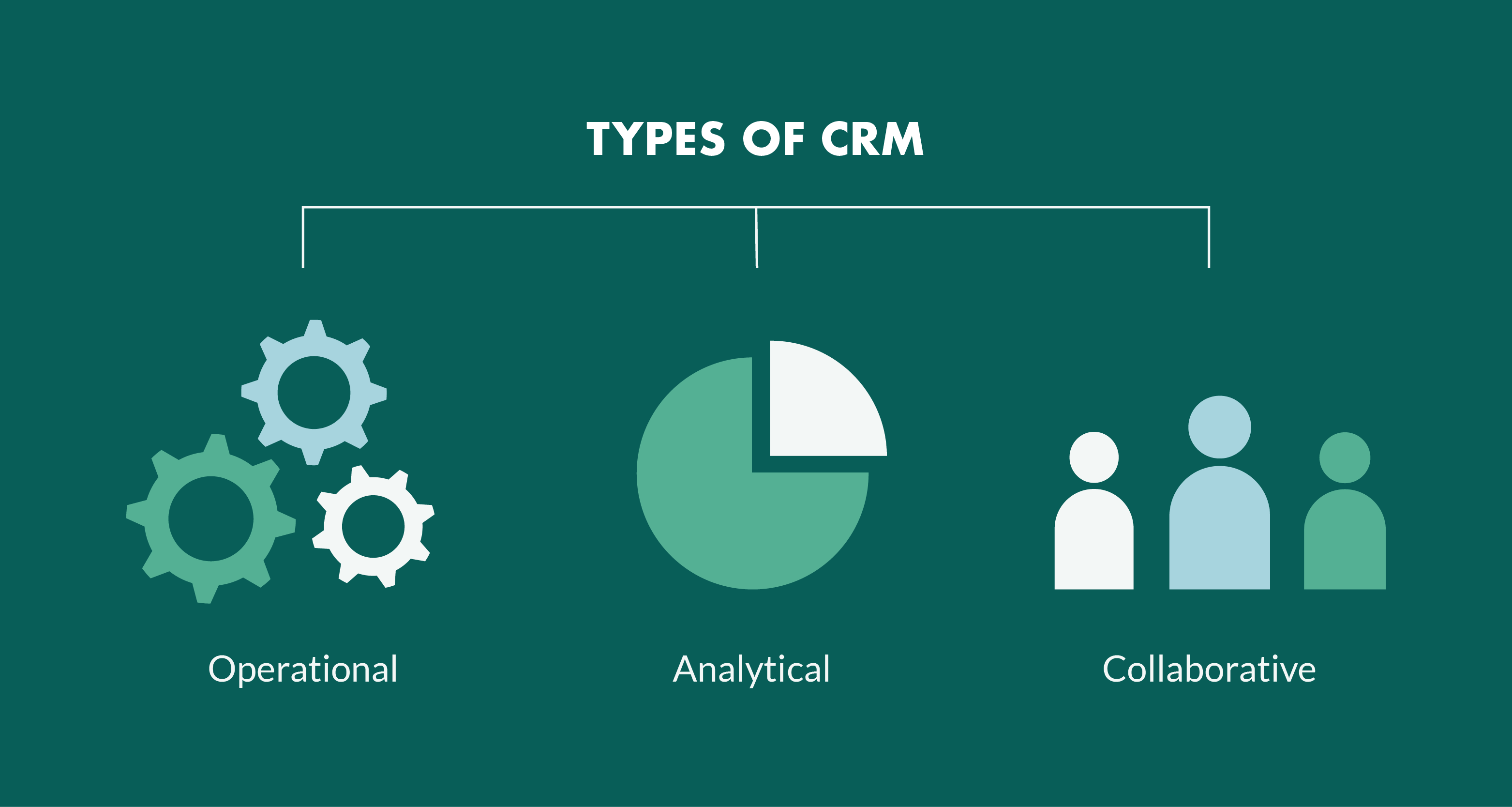
CRM Definition and Functions
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems are designed to help businesses manage and track their interactions with customers. They provide a centralized platform for storing customer data, tracking sales and marketing activities, and providing customer service. CRM systems can help businesses improve their customer relationships, increase sales, and provide better customer service.
Key Functions of CRM Systems
- Contact management:CRM systems allow businesses to store and track contact information for customers, leads, and prospects.
- Sales management:CRM systems can help businesses track sales opportunities, manage sales pipelines, and close deals.
- Marketing management:CRM systems can help businesses plan and execute marketing campaigns, track marketing results, and generate leads.
- Customer service management:CRM systems can help businesses track customer service requests, resolve customer issues, and provide customer support.
Benefits of CRM Systems
- Improved customer relationships:CRM systems can help businesses build stronger relationships with their customers by providing a central platform for tracking customer interactions.
- Increased sales:CRM systems can help businesses increase sales by providing a better understanding of customer needs and preferences.
- Better customer service:CRM systems can help businesses provide better customer service by providing a central platform for tracking customer issues and resolving them quickly.
Benefits of CRM in IT
CRM systems offer numerous advantages to IT organizations, particularly in enhancing customer service and support, streamlining sales and marketing processes, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Improved Customer Service and Support
- Centralized customer data: CRM systems consolidate customer information from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences.
- Enhanced case management: CRM systems enable IT support teams to track and manage customer cases efficiently, prioritizing urgent requests and providing timely resolutions.
- Personalized support: CRM systems allow IT professionals to tailor support interactions based on customer profiles, providing personalized assistance and building stronger relationships.
Streamlined Sales and Marketing Processes
- Lead generation and qualification: CRM systems help IT organizations generate and qualify leads, identifying potential customers and prioritizing those most likely to convert.
- Automated marketing campaigns: CRM systems automate marketing campaigns, sending targeted messages and nurturing leads through the sales funnel.
- Sales forecasting and analytics: CRM systems provide sales teams with real-time data on sales pipelines and customer behavior, enabling accurate forecasting and data-driven decision-making.
Improved Operational Efficiency
- Centralized communication: CRM systems serve as a central hub for communication between IT teams and customers, reducing the need for multiple channels and improving collaboration.
- Automated workflows: CRM systems automate repetitive tasks, such as case assignment and follow-up emails, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more complex tasks.
- Improved reporting and analytics: CRM systems provide comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling IT organizations to track key metrics, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions.
CRM Implementation Considerations
Implementing a CRM system in IT requires careful planning and execution. Here are key factors to consider:
Vendor Selection
- Research and evaluate potential vendors based on industry reputation, product capabilities, and customer support.
- Request demos and references to assess the vendor’s expertise and suitability.
- Consider the vendor’s experience in IT-specific CRM solutions.
Deployment Options
Choose between cloud-based or on-premises CRM solutions:
- Cloud-based:Hosted by the vendor, offers flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs.
- On-premises:Installed on your own servers, provides more control and customization options but requires higher upfront investment.
Implementation Process
Ensure a successful implementation by following these steps:
- Define project scope and objectives:Clearly Artikel the goals and desired outcomes of the CRM implementation.
- Involve stakeholders:Get buy-in and support from key stakeholders, including IT, business units, and end-users.
- Customize and integrate:Tailor the CRM system to meet specific IT needs and integrate it with existing systems.
- Train users:Provide comprehensive training to ensure user adoption and proficiency.
- Monitor and evaluate:Track performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize the CRM system’s effectiveness.
CRM Integrations and Data Management
Integrating CRM systems with other IT systems is crucial for streamlining operations and enhancing data visibility. By connecting CRM with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) solutions, businesses can automate order processing, inventory management, and financial transactions. Integrating CRM with help desk solutions enables seamless customer support by providing agents with a comprehensive view of customer interactions and issue history.
Effective CRM data management is essential for maintaining data accuracy, consistency, and security. Best practices include regular data cleansing, data deduplication, and data enrichment. Data analytics can be leveraged to gain insights into customer behavior, identify trends, and improve decision-making.
For instance, analyzing CRM data can reveal patterns in customer purchases, service requests, and interactions, allowing businesses to tailor personalized marketing campaigns and enhance customer experiences.
Challenges in CRM Data Management, Crm in it
- Data silos and lack of integration between different systems
- Data quality issues, such as duplicate records, incomplete data, and outdated information
- Security concerns related to data privacy and data breaches
Best Practices for CRM Data Management
- Establish clear data governance policies and procedures
- Implement data quality tools and processes for data cleansing and deduplication
- Integrate CRM with other systems to ensure data consistency and eliminate silos
- Provide training to users on proper data entry and management practices
CRM Trends and Future Directions

The CRM landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These trends are being driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the growing popularity of mobile devices, and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
One of the most significant trends in CRM is the move to cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based CRM systems offer a number of advantages over on-premises solutions, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and easier scalability. As a result, more and more businesses are moving their CRM systems to the cloud.
Another major trend in CRM is the growing popularity of mobile devices. Mobile CRM solutions allow sales and marketing teams to access their CRM data and applications from anywhere, at any time. This increased mobility is leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Impact of AI and ML on CRM Systems
AI and ML are having a major impact on CRM systems. AI-powered CRM systems can automate a variety of tasks, such as lead scoring, lead routing, and customer segmentation. This can free up sales and marketing teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
ML can also be used to improve the accuracy of CRM predictions. For example, ML algorithms can be used to predict the likelihood that a lead will convert into a customer. This information can be used to prioritize sales and marketing efforts.
The Future of CRM
The future of CRM is bright. CRM systems are becoming increasingly powerful and sophisticated, and they are playing an increasingly important role in IT organizations. As AI and ML continue to develop, CRM systems will become even more automated and intelligent.
In the future, CRM systems will be able to provide businesses with a complete view of their customers. This information will be used to improve customer service, marketing, and sales. CRM systems will also be able to help businesses identify and capitalize on new opportunities.
Ending Remarks
As CRM continues to evolve, IT organizations must embrace emerging trends and innovations to stay ahead of the curve. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into CRM systems is unlocking new possibilities for personalized customer experiences, predictive analytics, and automated workflows.
The future of CRM in IT holds immense promise, with its transformative capabilities poised to revolutionize the way organizations engage with their customers and drive business success.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is CRM?
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management, a system that helps organizations manage and track customer interactions and data.
How can CRM benefit IT organizations?
CRM can improve customer service and support, streamline sales and marketing processes, and enhance data management and analytics in IT organizations.
What are the key considerations for CRM implementation in IT?
Factors to consider include deployment options (cloud-based or on-premises), vendor selection, and ensuring a successful implementation process.